Table of Content
Based on the full sequence of monkeypox virus (AF380138) F3L gene published in GenBank, primers, TaqMan and MGB probes were designed and synthesized, and a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method for F3L gene was established. Using this method, a typical “s” curve could be amplified from the synthetic monkeypox virus F3L gene fragment (48048-48509bp), and the detection sensitivity of the 25 reaction system could reach 6.8 copies, but the corresponding amplification curve could not be amplified from chicken pox, goat pox and other viruses. The conclusion is this method could detect monkeypox virus rapidly, sensitively and specifically.
In 1958, monkeypox virus (MPV) was discovered in experimental macaques. Since the first report of human monkeypox cases in Zaire in 1970, sporadic cases have occurred in central and western African countries. A major outbreak occurred in Congo from February 1996 to October 1997, with 511 confirmed cases. The first monkeypox infection occurred in the United States from May to July 2003, and the source of infection was identified as groundhogs. The groundhogs were infected when they were co-reared with a Gambian giant rat imported from Africa that was infected with monkeypox virus, which has raised concerns about monkeypox around the world.
Monkeypox is a smallpox-like, zoonotic viral disease characterized by a skin rash. Humans, monkeys, other primates and rodents could all be infected with MONkeypox. The monkeypox virus genome is double-stranded DNA, about 197 kb in length, and the end of the genome contains an identical but opposite inverted terminal repeat. The content of guanine (G) + cytosine (C) in the monkeypox virus genome is very low, accounting for about 33%. With monkeypox spread in the world, it is necessary to look ahead and make technical reserves.
1. Materials and Methods
1.1 Materials
1.1.1 Viruses and Plasmids
The monkeypox-positive template was an artificially synthesized MPV (AF380138) F3L gene fragment (48048-48509 bp) inserted into plasmid pUC57, which was synthesized by Nanjing Shengxing Biotechnology Company. Mouse hemorrhagic fever, mouse lymphocytic choriomeningitis, mouse Sendai, mouse hepatitis, encephalomyelitis, polyoma, monkey herpes virus type I, mouse pox, sheep pox, chicken pox, pigeon pox and other viruses were purchased from Animal Standardization Office of China National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products.
1.1.2 Test Reagent
ExTaq enzymes, dNTPs, etc. were purchased from TaKaRa Company, TaqMan probes and primers were synthesized by TaKaRa Company, MGB probes and primers were synthesized by ABI Company, Lightcycler capillary and fluorescent PCR instrument were purchased from Roche Company.
1.2 Preparation of Templates
Directly take 200L virus solution into an Eppendorf tube, add 400txL lysate, 600IxL phenol/chloroform mixture and mix well, centrifuge at 12000r·min and 4°C for 3-5 min; take the supernatant and add 600IzL chloroform to mix, and centrifuge at 12000r·min for 5 min, then take the supernatant and add 0.8 times isopropanol to mix, and centrifuge at 10,000 r·min for 10 min; discard the supernatant, add 70% ethanol for washing, centrifuge for 3-5 min, and add 50LTE buffer to dissolve the precipitate after drying.
1.3 Real-time PCR
1.3.1 Primer and Probe Design
TaqMan probe method: TaqMan probes and primers were designed according to the F3L gene fragment, and both primers and probes were synthesized by TaKaRa Company. Primer sequence: 5GACAGGGrTAACAcC1_ICCAATAAAT一3, 5CAGTI’C—CGACGATACTCCTcCT一3. Probe: 5一FAM—TcTACGAcAATGGATGcTCAncACGGC—TARAM一3’.
MGB probe method: MGB probes and primers were designed according to the F3L gene fragment, and both primers and probes were synthesized by ABI Biological Company. Primer sequence: 5一TCGCGGGATACATCATCTATTATAGCA一3,5~GGTCTACGACAATGGATGCTGATA一3. Probe: 5一FAM—CACGGCCTACAGATYC—MGBNFQ一3.
1.3.2 PCR reaction TaqMan probe method
Using a 25L reaction system, take a Lightcycler capillary and add 10xExTaqBuffer2.5txL, dNTP (each 2.5mmol·L)3txL, MgC12(25mmol·L)3.5txL, primer (20lxmol·L一)each 0.5IAL, TaqMan probe (10Ixmol·L)1txL, ExTaq enzyme 0.25IAL, BSA (0.05%)1IxL, template DNA 1L, add ddHO to 25. After a brief centrifugation, PCR amplification was performed on a Lightcycler quantitative PCR instrument. Amplification conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 5 min; 95°C for 20s, 58°C for 1 min, 45 cycles.
MGB probe method: using a 25L reaction system, take a Lighteycler capillary and add 10~ExTaqBuffer2.5, dNTP (each 2.5mmol·L) 4txL, MgC1 (25mmol·L) 4.5txL, MGB primer and probe 1.25txL, ExTaq enzyme 0.25txL, BSA (0.05%) 1txL, template DNA 2txL, add ddH2O to 25L. After a brief centrifugation, PCR amplification was performed on a Lightcycler quantitative PCR instrument. Amplification conditions: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 10 min; 95°C for 15s, 60°C for 1 min, 45 cycles.
1.3.3 Specificity test
According to the method 1.2, extract mouse hemorrhagic fever, mouse lymphocytic choriomeningitis, mouse Sendai, mouse hepatitis, encephalomyelitis, polyoma, monkey herpes virus type I, mouse pox, sheep pox, fowl pox, pigeon The DNA of pox and other viruses was amplified by fluorescent PCR to observe the specificity of the reaction.
1.3.4 Sensitivity test
Take the positive template of known concentration and carry out 10-fold gradient dilution, respectively take the positive template of each dilution, carry out fluorescence PCR amplification according to the two methods of 1.3.2, and observe the sensitivity of the reaction.
1.3.5 Detection of samples
A total of 43 monkey throat swab samples were collected from Nanjing Hongshan Zoo and Suzhou Xishan Experimental Animal Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the samples were detected by the above two fluorescent PCR methods respectively.
2. Results and Analysis
2.1 Fluorescence PCR amplification results
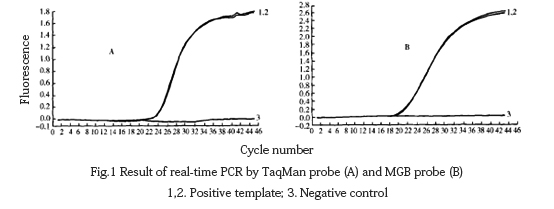
Use the optimized reaction system to amplify the positive template and analyze it with Lighteyeler Software Version 3.5 software. It could be seen from the figure that the amplification curve of the positive template is a typical “s” shape (Fig. 1), while water as a negative control template could not be used. Specific amplification signals were detected.
2.2 Specificity test results
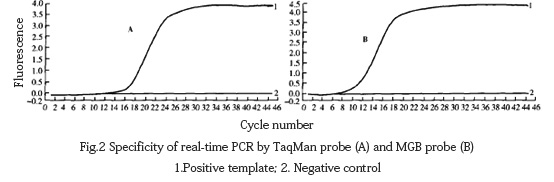
The DNA of fowl pox and other viruses was extracted and amplified by fluorescent PCR using TaqMan probe method and MGB probe method respectively. It was found that except for the positive template with specific amplification curve, other viruses had no amplification curve (Fig. 2).
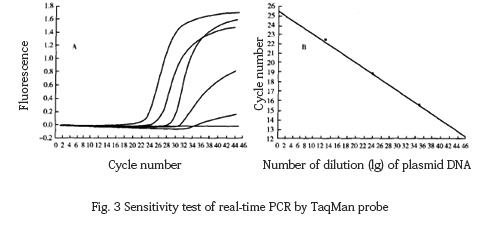
2.3 Sensitivity test results
TaqMan probe fluorescent PCR was used to amplify the 10-fold dilution of the target template, and it was found that the lower limit of detection was 68 copies, and the regression equation was Y=−3.329x+5.587(r:−1.00)(Fig. 3).
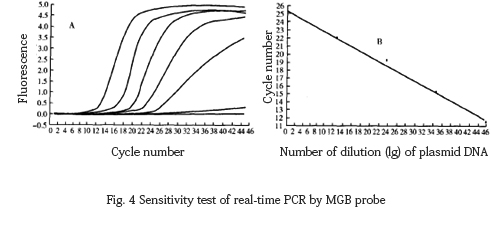
The 10-fold dilution of the target DNA fragment was amplified by MGB probe fluorescence PCR, and the lower limit of detection was found to be 6.8 copies, and the correlation equation was Y=−3.367x+8.524, r=−1 .00 (Fig. 4).
3. Discussion
Virus isolation and identification is a classic method for diagnosing monkeypox, but monkeypox virus is a biosafety grade IV biological factor, which requires extremely high laboratory biosafety and the detection period is too long. Due to the antigenic crossover between monkeypox virus and pox virus, the specificity of serological method is not enough; PCR method is used to detect monkeypox virus nucleic acid, which is highly sensitive and fast, and the result could be obtained in only a few hours. In this regard, foreign scholars have done a lot of research. Neubauer et al., Meyer et al. used the characteristics of ATI protein gene to amplify to detect monkeypox virus. The hemagglutinin gene is unique to orthopoxvirus and could be distinguished from other poxviruses, and the hemagglutinin gene of monkeypox virus is relatively conservative. Ropp et al. and Lbrahim et al used amplified hemagglutinin gene sequences to detect monkeypox virus. However, there are not many similar reports in the country.
Due to the lack of monkeypox virus species in my country, the F3L fragment containing the specific monkeypox virus target gene was synthesized artificially with reference to literature in this experiment, and inserted into the plasmid as a mock positive template for monkeypox virus detection. In this paper, specific TaqMan and MGB probes and primers were designed for the F3L fragment sequence, and a real-time quantitative PCR method for rapid detection and diagnosis of monkeypox virus was established. The test proved that both probes could meet expectations Effect.
TaqMan was designed according to the feature of low G+C content in monkeypox virus genome. MGB probes could improve the value of the probes, but MGB probes are patented by ABI and must be synthesized abroad, which are expensive and time-consuming. To this end, a set of TaqMan probes were optimized and designed in this experiment for the real-time PCR detection of monkeypox virus, which also achieved good results.
At the same time, the fluorescent quantitative PCR method is more time-saving and specific because it does not require electrophoresis analysis, reduces cross-contamination, and could accurately quantitatively analyze samples.
转自体外诊断IVD知识库
Recent Posts
Earth Day in the Lab: GenFollower’s Eco‑Driven Innovations for Sustainable Science
What is Earth Day? Earth Day began in the United States in the early 1970s, when a burgeoning environmental movement on college campuses sought to awaken public consciousness towards the fragility of our planet. [...]
What is Cell Therapy Manufacturing?Essentials and manufacturing processes for cell therapies
Cell therapy is rewriting the rules of modern medicine. Imagine a treatment that uses a patient’s own immune cells, reprogrammed in a lab to hunt down and destroy cancer—this is no longer science fiction [...]
Why use filter pipette tips? A Comprehensive Guide to Filter Pipette Tips
In laboratory workflows, unseen threats like aerosol contamination, residual liquid carryover, and cross-contamination can silently sabotage experimental results. This is where filter pipette tips step in—not just as disposable tools for liquid handling, but [...]